Simple Transistor Amplifier Circuit Explained Circuit Diagram
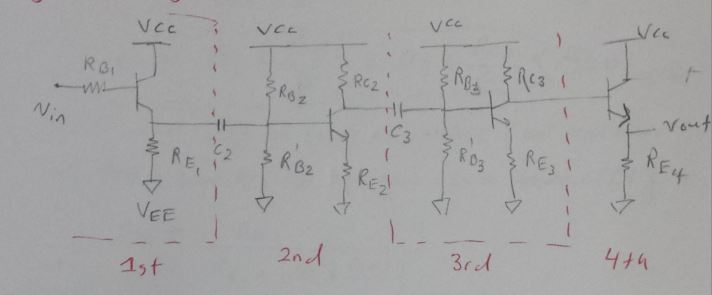
Simple Transistor Amplifier Circuit Explained Circuit Diagram Transistor Amplifier Circuits Unit 1 - Introduction to Transistor Amplifiers 2 NEW TERMS AND WORDS Multistage - an amplifier circuit that uses more than one active component (transistor). active component - a circuit component that controls gain or directs current flow. gain - the amount by which an amplifier increases signal voltage, current, or power; expressed as The choice of the transistor depends on the frequency range and the power level. Here, we are making a small signal AF amplifier and can use any of the hundreds of transistors. So let's use the well-known BC337. How the circuit works. Our design begins with a look inside the transistor itself. The Base of the transistor used in a common emitter amplifier is biased using two resistors as a potential divider network. This type of biasing arrangement is commonly used in the design of bipolar transistor amplifier circuits and greatly reduces the effects of varying Beta, ( β) by holding the Base bias at a constant steady voltage. This

Transistor Amplifier P1 A simple explanation of how a transistor works in a circuit, and how to connect transistors to create a number of different circuits. No mathematics and no complex wording. Just a completely different approach you can understand . . . TOPICS: Adjustable Current Power Supply Adjusting The Stage Gain AF Detector

PDF Physics 222 Circuit Diagram
In this case if we applied the input signal of 0 degree phase then output will be obesrved to be Phase of 180 degree. The common-emitter amplifier design is called an inverting amplifier. Examples. Q1. The output resistance of a common base transistor amplifier is 100 kΩ, while the input resistance is 10 Ω. One kΩ is the collector load.
![Transistor amplifier circuit [12]. Circuit Diagram](https://www.researchgate.net/publication/266894223/figure/download/fig2/AS:295736378970114@1447520455139/Transistor-amplifier-circuit-12.png)
Transistor amplifiers are circuits that are used to amplify weak audio, DC, or AC signals, and have a wide range of applications. When amplifying AC signals using a transistor amplifier, both voltage and current can be amplified simultaneously. There are three configurations of transistor amplifiers: Common-base amplifiers. Common-emitter

PDF Transistor Amplifier Circuits Circuit Diagram
K. Webb ECE 322 4 BJT Amplifier Circuits Recall the two functional pieces of a BJT amplifier: Bias network Sets the DC operating point of the transistor Ensures the BJT remains in the forward-active region Signal path Biasing. Network Signal path Sets the gain of the amplifier circuit Significant overlap between the two parts